Learn how to build efficient DevOps pipelines, automate deployments, and implement best practices for continuous integration and delivery in modern software development teams.
Why DevOps Automation Matters Today
DevOps automation has revolutionized how development teams deliver software. By eliminating manual processes and creating consistent workflows, organizations reduce deployment time from weeks to minutes while maintaining high quality standards. The transformation goes beyond simple time savings, fundamentally changing how teams collaborate and deliver value to customers.
The key to successful DevOps lies in automating repetitive tasks that consume valuable development time. When teams automate testing, builds, and deployments, they can focus on creating innovative features instead of managing infrastructure complexities. This shift allows developers to spend 70% more time on feature development rather than operational tasks.
Modern businesses that implement DevOps automation typically experience 60% faster deployment cycles and 50% fewer production failures. These improvements directly translate to competitive advantages and improved customer satisfaction. Companies like Netflix and Amazon deploy thousands of times per day, demonstrating the scalability and reliability that proper automation enables.
The cultural impact of DevOps automation cannot be understated. Teams develop greater confidence in their releases, knowing that automated processes catch errors before they reach production. This confidence encourages experimentation and innovation, as the safety net of automation reduces the fear of breaking systems.
Building Effective CI/CD Pipelines
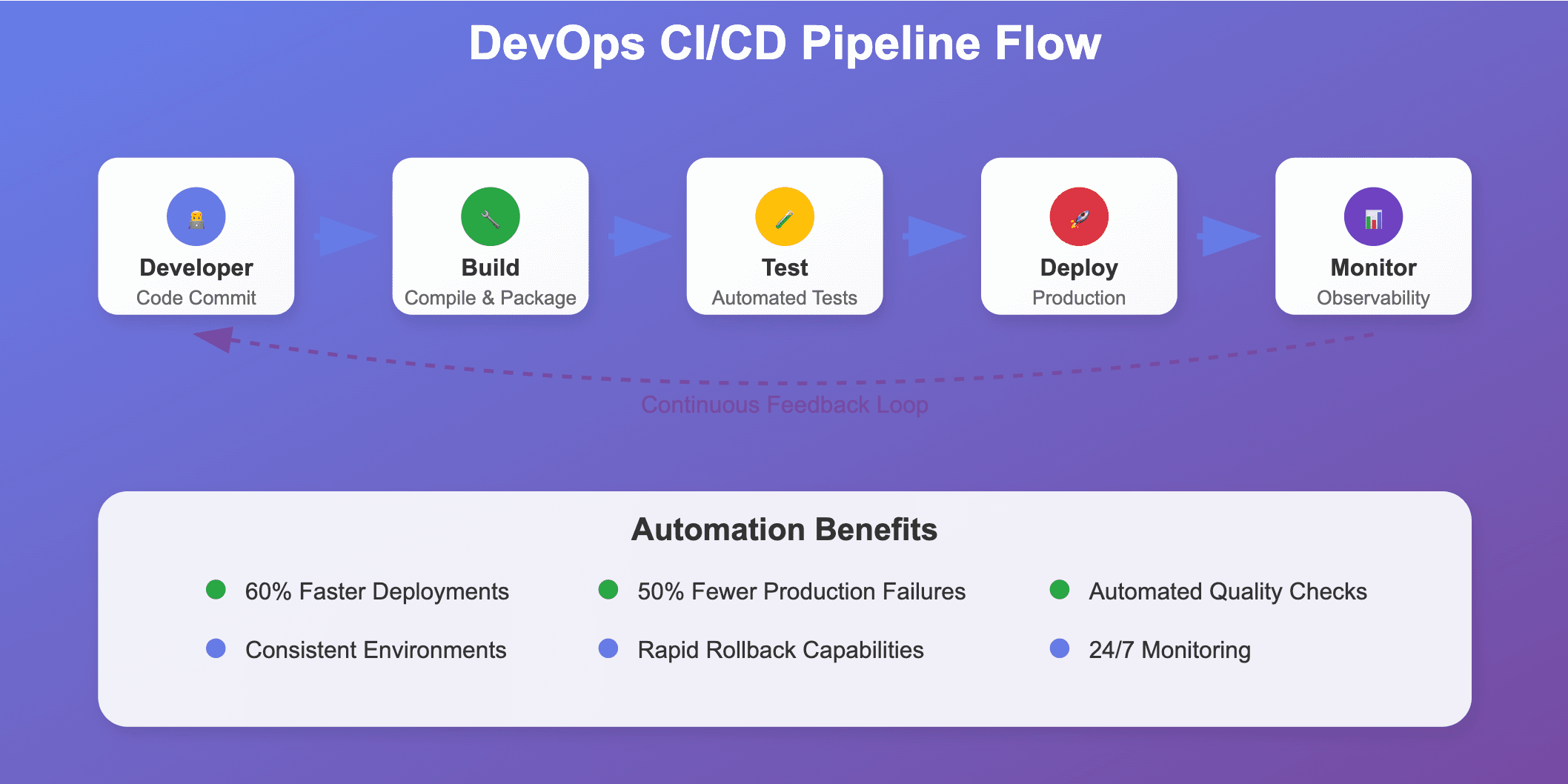
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) forms the backbone of modern DevOps practices. Your pipeline should automatically trigger when developers commit code, running tests and deploying successful builds to production environments. The entire process should complete without human intervention for routine changes.
Start with a simple three-stage pipeline: build, test, and deploy. Each stage should have clear success criteria and automated validation steps. Failed builds should immediately notify the development team, preventing broken code from advancing through the pipeline. This immediate feedback loop helps developers fix issues while the context is fresh in their minds.
Advanced pipelines incorporate multiple testing phases, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end testing scenarios. Each test type serves a specific purpose in validating application functionality and preventing regressions from reaching production environments. Automated testing should cover at least 80% of your codebase to ensure comprehensive validation.
Infrastructure as Code Implementation
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) treats your servers and environments like software code. Tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation allow you to define infrastructure requirements in version-controlled files, ensuring consistent environments across development, staging, and production. This approach eliminates configuration drift and human error in infrastructure management.
Teams can deploy identical infrastructure configurations with confidence, knowing that all environments match exactly. Version control for infrastructure enables rollback capabilities and change tracking, providing the same benefits that developers enjoy with application code. Infrastructure changes become reviewable, testable, and auditable.
Docker containers provide consistent application environments regardless of the underlying infrastructure. Containerization ensures that applications run identically across different systems, eliminating the common "it works on my machine" problem. Container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes add automatic scaling, load balancing, and self-healing capabilities.
Microservices architecture benefits significantly from containerization, as each service can be independently deployed and scaled. This independence allows teams to move faster while reducing the risk of one service affecting others. Container registries provide centralized storage and distribution of application images.
Monitoring and Alerting Best Practices
Effective monitoring provides visibility into application performance and infrastructure health. Implement comprehensive logging and metrics collection that enables proactive issue detection before users experience problems. Modern monitoring solutions use machine learning to identify anomalies and predict potential failures.
Set up automated alerts for critical metrics like response time, error rates, and resource utilization. Configure alerts to notify the right team members at appropriate severity levels, preventing alert fatigue while ensuring rapid response to genuine issues. Implement escalation procedures for critical alerts that require immediate attention.
Distributed tracing helps identify performance bottlenecks across microservices architectures. Tools like Jaeger and Zipkin provide detailed insights into request flows, helping teams optimize application performance. This visibility becomes crucial as applications grow in complexity and span multiple services.
Security Integration Throughout the Pipeline
Security scanning should be automated within your CI/CD pipeline rather than treated as a separate process. Implement vulnerability scanning for dependencies, container images, and infrastructure configurations at every stage of development. This shift-left approach to security reduces risks while maintaining development velocity.
Automated security checks catch potential issues early when they're easier and cheaper to fix. Static Application Security Testing (SAST) analyzes source code for security vulnerabilities, while Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tests running applications for security flaws. Both approaches should be integrated into your pipeline.
Access control and secret management require careful attention in automated environments. Use dedicated tools for managing API keys, passwords, and certificates, ensuring that sensitive information never appears in code repositories. Implement role-based access control to limit who can modify pipeline configurations and deployment targets.
Compliance automation helps organizations meet regulatory requirements without manual overhead. Tools can automatically generate compliance reports and ensure that security policies are consistently applied across all environments. This automation reduces the burden on security teams while maintaining necessary compliance standards.
Advanced Deployment Strategies
Blue-green deployments minimize downtime by maintaining two identical production environments. Deploy new versions to the inactive environment, test thoroughly, then switch traffic to the new version. This approach enables instant rollback if issues arise and eliminates deployment downtime.
Canary releases gradually roll out new features to a subset of users before full deployment. This strategy allows teams to validate new functionality with real users while limiting the blast radius of potential issues. Automated monitoring can trigger rollbacks if error rates exceed acceptable thresholds.
Feature flags provide additional control over functionality rollout, enabling teams to toggle features on or off without deploying new code. This approach supports A/B testing and gradual feature adoption across user segments, reducing the risk of negative user impact.
Getting Started with DevOps Automation
Begin your DevOps journey by identifying the most time-consuming manual processes in your current workflow. Start with automating your build and test processes, then gradually expand to include deployment and monitoring automation. This incremental approach reduces risk while building team confidence.
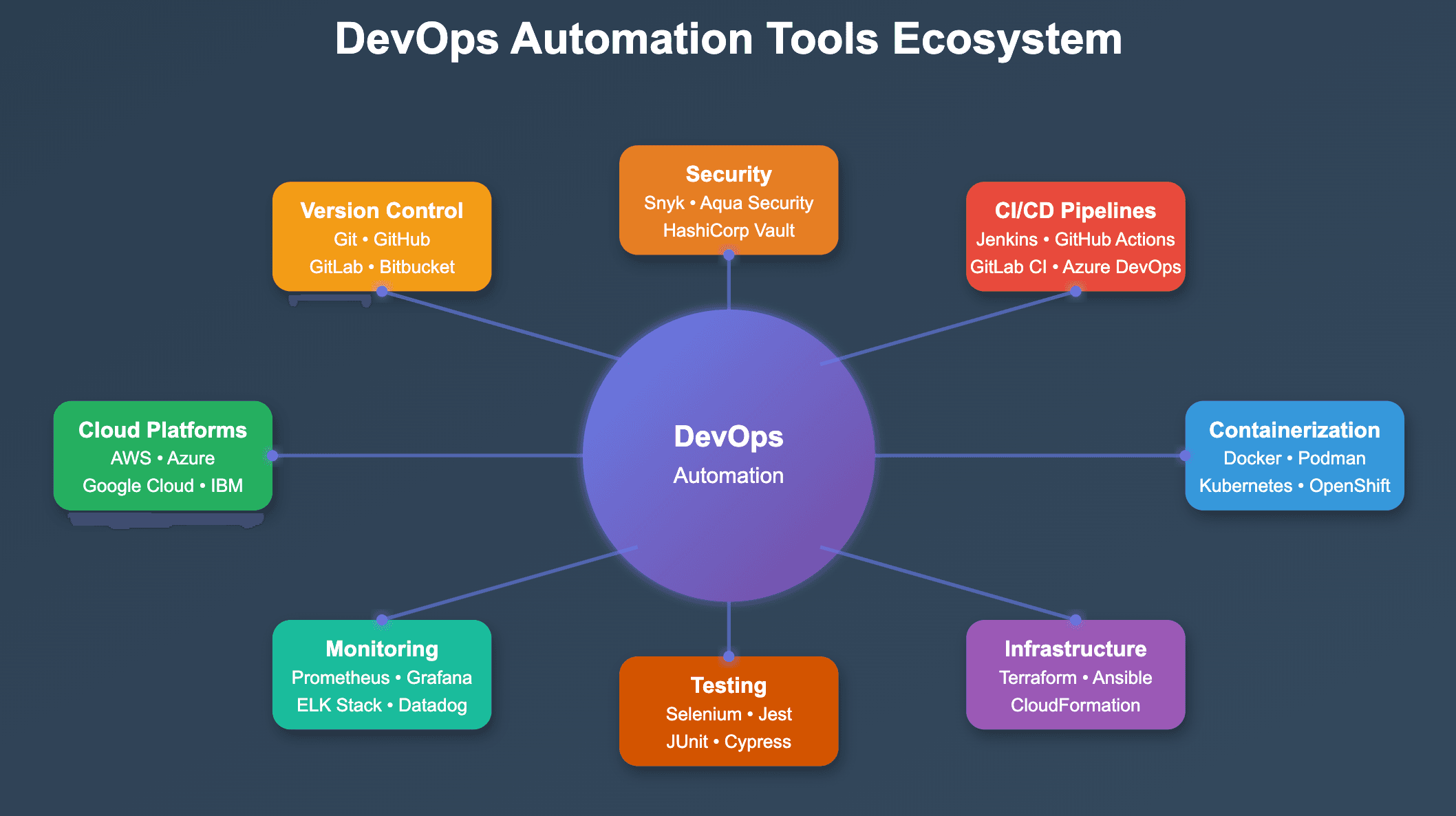
Choose tools that integrate well with your existing technology stack. Popular options include Jenkins for CI/CD, Docker for containerization, and Kubernetes for orchestration. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide comprehensive DevOps toolsets with managed services that reduce operational overhead.
Focus on creating simple, reliable automation before adding complexity. A basic automated pipeline that works consistently is more valuable than a complex system that frequently breaks. Measure the impact of each automation effort and continuously improve based on results.
Team training and cultural change are equally important as technical implementation. Ensure that all team members understand the benefits of automation and have the skills necessary to maintain and improve your DevOps processes. Invest in training programs and encourage knowledge sharing across teams.
Start small, measure results, and continuously improve your automation practices. Successful DevOps transformation takes time, but the benefits of increased productivity and reliability make the investment worthwhile. Organizations that commit to this transformation position themselves for long-term success in competitive markets.
